Back
Constipation in Men, Why can't I poop?
By Shannon Strauch, PTA, STMT-1 on 8/1/2024

Introduction
Constipation is a common issue that can affect anyone, but understanding its specific causes and mechanics in men can help in addressing and managing it effectively. This blog will delve into why constipation occurs in men, the mechanics of bowel movements, the role of the colon, pelvic floor muscles, and how pelvic floor therapy can provide relief. We will also explore the fascial connections to muscles and the sacrum, which play a crucial role in the overall functionality of the pelvic floor.
Causes of Constipation in Men
Dietary Factors:
Low fiber intake
Inadequate hydration
Lifestyle Factors:
Lack of exercise
Ignoring the urge to defecate
Medical Conditions:
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
Diabetes
Neurological disorders
Mechanics of Bowel Movements
Digestive Process:
Begins with ingestion and ends with elimination.
Role of the Colon:
Absorbs water from stool.
Forms and stores stool until ready for elimination.
Defecation Reflex:
Involves coordination of muscles in the rectum and anus.
Triggered when stool enters the rectum, causing the urge to defecate.
Pelvic Floor Muscles and Their Role
Anatomy:
Comprises muscles that support the bladder, intestines, and rectum.
Important for maintaining continence and supporting pelvic organs.
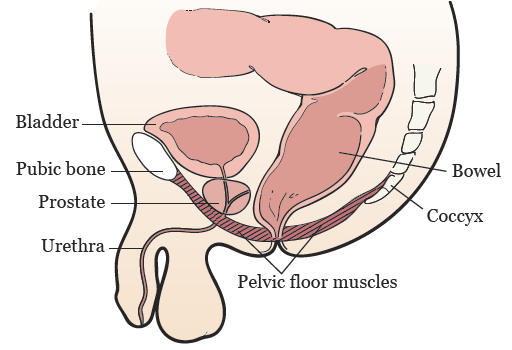
Support in Defecation:
Muscles must relax to allow stool to pass.
Involves coordination with abdominal muscles to increase intra-abdominal pressure.
Coordination with Abdominal Muscles:
Helps in effective bowel movements.
Ensures proper pressure and timing during defecation.
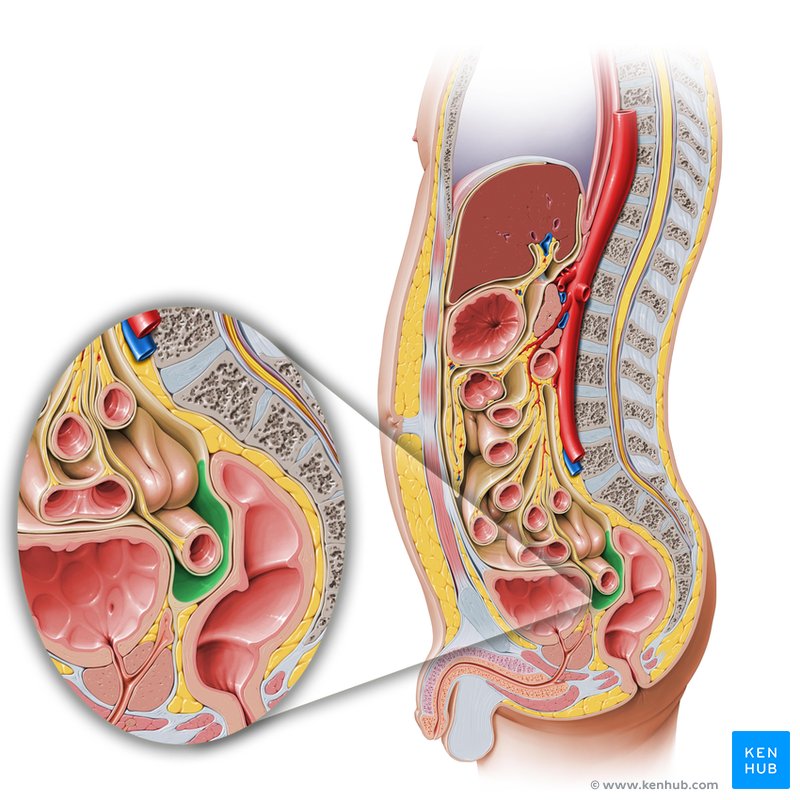
Fascial Connections to Muscles and Sacrum
Fascial Network:
Fascia is a connective tissue that surrounds muscles, organs, and other structures.
Provides structural support and facilitates movement.
Pelvic Fascia:
Connects pelvic floor muscles to the sacrum and other pelvic structures.
Plays a crucial role in maintaining pelvic stability and function.
Sacrum Connection:
The sacrum is a triangular bone at the base of the spine.
Acts as an anchor point for pelvic floor muscles and fascia.
Ensures proper alignment and support during bowel movements.
How Pelvic Floor Therapy Can Help
Evaluation and Assessment:
Identifying specific issues with muscle strength or coordination.
Understanding the role of fascia in pelvic floor dysfunction.
Treatment Approaches:
Exercises to strengthen or relax pelvic floor muscles.
Techniques to improve fascial mobility and reduce tension.
Biofeedback Techniques:
Training to enhance muscle coordination and control.
Visual and auditory feedback to aid in proper muscle function.
Behavioral Changes:
Education on dietary and lifestyle modifications.
Guidance on proper bowel habits and techniques.
Conclusion
Constipation in men can result from various factors, including diet, lifestyle, and medical conditions. Understanding the mechanics of bowel movements and the role of the colon, pelvic floor muscles, and fascial connections can help in managing and alleviating symptoms. Pelvic floor therapy offers effective solutions through targeted exercises, biofeedback, and education on healthy habits. If you experience chronic constipation, reach out to us at Pelvic Health Center in Madison, NJ to set up an evaluation and treatment! Feel free to call us at 908-443-9880 or email us at receptionmadison@pelvichealthnj.com.
Read More:
How Chronic Pelvic Congestion in Men Contributes to Prostatitis By Shannon Strauch, PTA, STMT-1 on 12/11/2024 How lymphatic issues can cause symptoms of prostatitis Prostatitis and Tight Pelvic Floor Muscles: A Comprehensive Guide By Shannon Strauch, PTA, STMT-1 on 12/10/2024 How a tight pelvic floor can be the reason for prostatitis symptoms
Are you ready to live pain free?
Request An Appointment