Back
Sports Hernias: Anatomy, Mechanism of Injury, and Treatment Options
By Dr. Christine Martirez PT, DPT on 4/2/2024
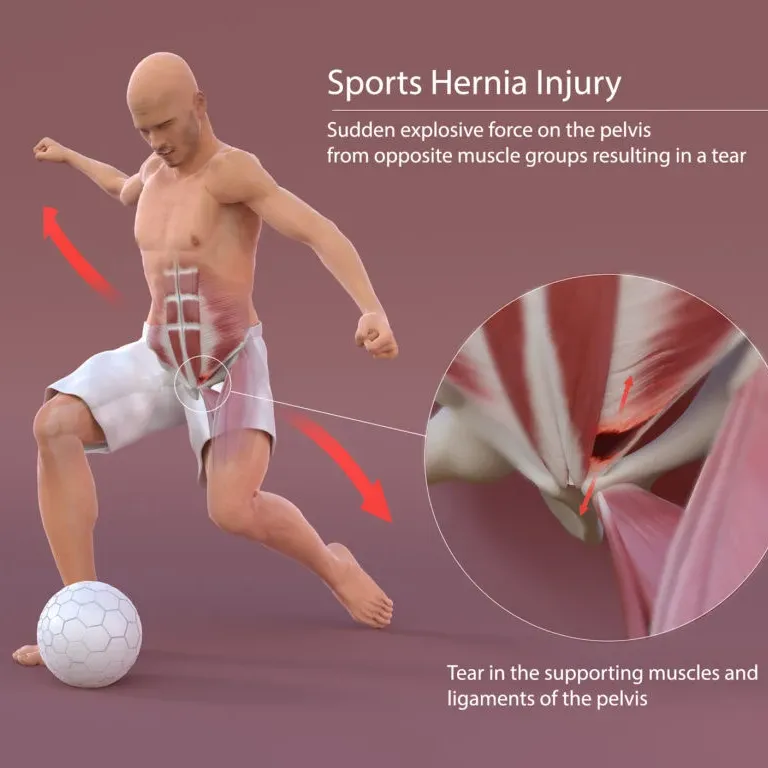
Sports hernias, also known as athletic pubalgia, can be debilitating for athletes, causing chronic inguinal or pubic area pain that is exertional and not explainable by a palpable hernia or other medical diagnosis. In this blog post, we'll explore the intricate anatomy involved in sports hernias, the mechanism of injury, surgical treatment options, and the role of pelvic floor physical therapy in managing this condition.

Unraveling the Anatomy of Sports Hernias
Anatomical Structures Involved:
Sports hernias involve the muscles, tendons, and ligaments of the inguinal and pubic regions. Key structures include the rectus abdominis, adductor muscles (particularly the adductor longus), inguinal ligament, and pubic symphysis.Actions of Muscles:
The rectus abdominis is responsible for flexing the trunk, while the adductor muscles are involved in bringing the thigh towards the midline of the body. These muscles work in tandem during activities such as running, cutting, and kicking.Origin and Insertion of Muscles:
The rectus abdominis originates from the pubic symphysis and inserts into the costal cartilages of the ribs and the xiphoid process of the sternum. The adductor muscles originate from the pelvis and insert into the femur.
Mechanism of Injury
Abdominal Hyperextension and Thigh Hyperabduction:
Sports hernias often occur due to forces that shear the pubic symphysis as a pivot point for force transfer. Abdominal hyperextension and thigh hyperabduction during activities can strain the muscles and ligaments of the inguinal and pubic regions.Progressive Micro-Tearing of Rectus Abdominis:
Another mechanism involves progressive micro-tearing of the rectus abdominis at its insertion point on the pubis. Repetitive stress from athletic movements can lead to weakening and damage of the muscle fibers.
Surgical Treatment Options
Hernia Repair Surgery:
Surgical intervention may be necessary for severe cases of sports hernias that do not respond to conservative treatment. Hernia repair surgery aims to strengthen the weakened or damaged tissues and restore stability to the pelvic region.Mesh Implantation:
In some cases, surgeons may use mesh implants to provide additional support and reinforcement to the affected area. This can help prevent recurrence of the hernia and facilitate the healing process.
The Role of Pelvic Floor Physical Therapy
Comprehensive Assessment:
Pelvic floor physical therapists conduct a comprehensive assessment to evaluate muscular imbalances, pelvic alignment, and movement patterns contributing to sports hernias. This may include palpation, functional movement tests, and pelvic floor muscle assessment.Targeted Rehabilitation Exercises:
Therapists prescribe personalized exercises to address muscle weaknesses, imbalances, and dysfunctions in the pelvic region. This may include strengthening exercises for the core muscles, hip stabilizers, and pelvic floor muscles.Manual Therapy Techniques:
Manual therapy techniques such as myofascial release, trigger point therapy, and joint mobilization may be used to reduce tension and improve mobility in the affected muscles and soft tissues.Movement Re-Education:
Pelvic floor physical therapy includes movement re-education to optimize biomechanics and reduce strain on the injured tissues. Therapists provide guidance on proper body mechanics during athletic activities and functional tasks.
A Multidisciplinary Approach to Recovery
Sports hernias can pose significant challenges for athletes, but with a multidisciplinary approach to treatment, recovery is possible. By understanding the anatomy, mechanism of injury, and treatment options for sports hernias, athletes can make informed decisions about their care. Whether opting for surgical intervention or conservative management with pelvic floor physical therapy, the goal is to restore function, alleviate pain, and return to peak athletic performance. If you're experiencing symptoms of a sports hernia, consult with a healthcare provider to explore your treatment options and embark on the path to recovery.
If you're suffering from symptoms similar to a sports hernia, please reach out to us at Pelvic Health Center in Madison, NJ to set up an evaluation and treatment! Feel free to call us at 908-443-9880 or email us at receptionmadison@pelvichealthnj.com.
Read More:
How Chronic Pelvic Congestion in Men Contributes to Prostatitis By Shannon Strauch, PTA, STMT-1 on 12/11/2024 How lymphatic issues can cause symptoms of prostatitis Prostatitis and Tight Pelvic Floor Muscles: A Comprehensive Guide By Shannon Strauch, PTA, STMT-1 on 12/10/2024 How a tight pelvic floor can be the reason for prostatitis symptoms
Are you ready to live pain free?
Request An Appointment