Back
Understanding Penis Anatomy and How PFPT Can Treat Dysfunctions
By Dr. Zarina Vitebsky, DPT, MSPT, PRPC, TPS, LPF, DN on 10/29/2023
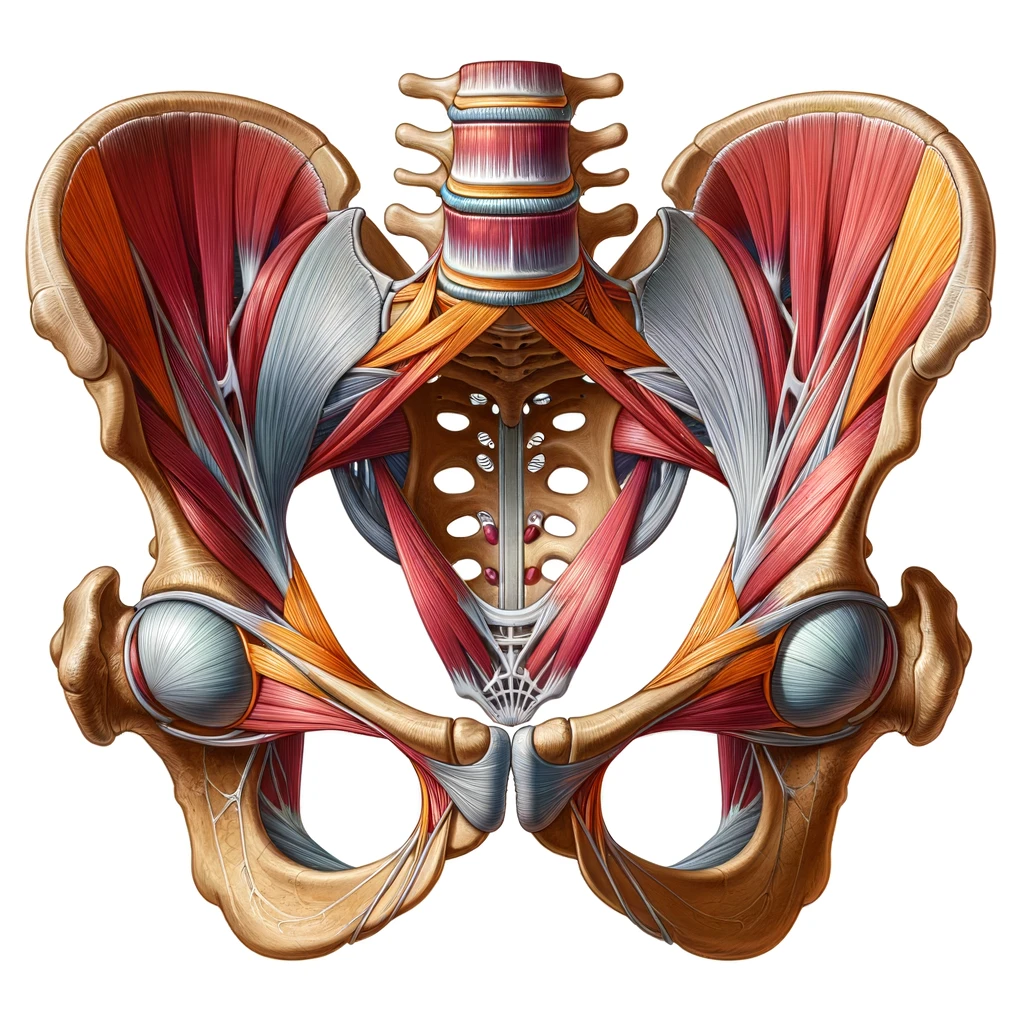
Overview
The penis is a male reproductive organ that is responsible for sexual function and urination. It is composed of three main parts: the root, the shaft, and the glans. The root is the base of the penis, which attaches to the pelvic bones. The shaft is the main body of the penis, and the glans is the rounded tip. The penis also contains three chambers of spongy tissue that fill with blood during an erection.
Importance of Understanding Penis Anatomy
Understanding penis anatomy is crucial for overall sexual health and function. It allows individuals to identify any potential issues or dysfunctions and seek appropriate treatment. It also helps in communication with healthcare professionals, as well as partners, about any concerns or problems related to the penis.
Introduction to Potential Dysfunctions
There are various potential dysfunctions that can affect the penis, including erectile dysfunction, premature ejaculation, and Peyronie's disease. Erectile dysfunction is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection, while premature ejaculation is the inability to control ejaculation. Peyronie's disease is a condition where scar tissue forms in the penis, causing it to curve during an erection.
Overview of How Pelvic Floor Physical Therapy (PFPT) Can Treat Dysfunctions
Pelvic floor physical therapy (PFPT) is a specialized form of physical therapy that focuses on the muscles, ligaments, and tissues in the pelvic floor. It can be used to treat various dysfunctions related to the penis, such as erectile dysfunction, premature ejaculation, and Peyronie's disease. PFPT can help improve blood flow, strengthen pelvic floor muscles, and address any underlying issues that may be causing the dysfunction.
Penis Anatomy
External Structures
The external structures of the penis include the shaft, glans, and foreskin. The shaft is the main part of the penis and is made up of three cylindrical columns of tissue called the corpora cavernosa. The glans, also known as the head of the penis, is the sensitive, rounded end of the penis. The foreskin is a retractable fold of skin that covers the glans in uncircumcised males.
Internal Structures
The internal structures of the penis include the corpora cavernosa, corpus spongiosum, and urethra. The corpora cavernosa are two chambers that run along the length of the penis and are responsible for the majority of the penis's rigidity during an erection. The corpus spongiosum is a smaller chamber that surrounds the urethra, which is the tube that carries urine and semen out of the body.
Blood Supply and Nerve Innervation
The penis receives its blood supply from the internal pudendal artery, which branches off from the internal iliac artery. The nerve innervation of the penis comes from the pudendal nerve, which is responsible for sensation and motor control of the pelvic floor muscles.
Role of Pelvic Floor Muscles in Penis Function
The pelvic floor muscles play a crucial role in penis function, including maintaining erections, controlling ejaculation, and supporting the bladder and bowel. Dysfunction in these muscles can lead to issues such as erectile dysfunction, premature ejaculation, and urinary incontinence. Pelvic floor physical therapy (PFPT) can help treat these dysfunctions by strengthening and relaxing the pelvic floor muscles through exercises and manual therapy techniques.
Potential Dysfunctions
Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual activity. It can be caused by various factors such as physical conditions (e.g. diabetes, heart disease), psychological factors (e.g. stress, anxiety), and lifestyle choices (e.g. smoking, excessive alcohol consumption).
ED can have a significant impact on sexual function and relationships. It can lead to feelings of inadequacy, frustration, and low self-esteem for the individual experiencing it. It can also cause strain and tension in intimate relationships.
Psychological factors can also play a role in ED. Performance anxiety, relationship issues, and past traumas can all contribute to difficulties with achieving or maintaining an erection.
Premature Ejaculation
Premature ejaculation (PE) is a common sexual dysfunction where a man ejaculates sooner than he or his partner would like during sexual activity. It can be caused by physical factors such as hormonal imbalances or inflammation of the prostate, as well as psychological factors such as anxiety, guilt, or relationship issues.
PE can have a significant impact on sexual function and relationships. It can lead to feelings of frustration, embarrassment, and shame for the individual experiencing it. It can also cause strain and tension in intimate relationships.
Psychological factors can also play a role in PE. Performance anxiety, relationship issues, and past traumas can all contribute to difficulties with controlling ejaculation.
Peyronie's Disease
Peyronie's disease is a condition where scar tissue forms in the penis, causing it to curve or bend during an erection. It can be caused by trauma to the penis, genetics, or underlying medical conditions such as diabetes or high blood pressure.
Peyronie's disease can have a significant impact on sexual function and relationships. It can cause pain during erections, difficulty with penetration, and feelings of embarrassment or shame. It can also lead to strain and tension in intimate relationships.
Psychological factors can also play a role in Peyronie's disease. The physical changes in the penis can cause feelings of insecurity and low self-esteem, which can affect sexual function and relationships.
Other Dysfunctions
In addition to the above dysfunctions, there are other potential dysfunctions that can affect the penis. These include priapism, a prolonged and painful erection, and penile fracture, a rare but serious injury that occurs when the erect penis is bent forcefully.
Both priapism and penile fracture can have a significant impact on sexual function and relationships. They can cause physical pain and discomfort, as well as psychological distress and strain in intimate relationships.
Role of Pelvic Floor Physical Therapy
Definition and Goals of PFPT
Pelvic Floor Physical Therapy (PFPT) is a specialized form of physical therapy that focuses on the muscles, ligaments, and tissues of the pelvic floor. The pelvic floor is a group of muscles that support the pelvic organs, including the bladder, rectum, and penis. The main goal of PFPT is to improve the function and strength of these muscles to alleviate symptoms and improve overall quality of life.
How PFPT Can Help with Penis Dysfunctions
Penis dysfunctions, such as erectile dysfunction, premature ejaculation, and pain during intercourse, can be caused by a variety of factors, including pelvic floor muscle dysfunction. PFPT can help by addressing any underlying issues with the pelvic floor muscles, which may be contributing to these dysfunctions. By improving the strength and function of these muscles, PFPT can help improve sexual function and alleviate symptoms.
Techniques Used in PFPT for Penis Dysfunctions
There are several techniques used in PFPT to address penis dysfunctions:
Manual Therapy: This involves hands-on techniques to release tension and improve mobility in the pelvic floor muscles. This can include massage, stretching, and trigger point release.
Biofeedback: This technique uses sensors to measure muscle activity and provides visual or auditory feedback to help patients learn how to relax and contract their pelvic floor muscles properly.
Therapeutic Exercises: Specific exercises are prescribed to strengthen and improve the function of the pelvic floor muscles. These may include Kegels, squats, and other targeted movements.
Benefits of PFPT for Penis Dysfunctions
PFPT can offer numerous benefits for those experiencing penis dysfunctions:
Improved sexual function and satisfaction
Reduced pain and discomfort during intercourse
Increased bladder and bowel control
Improved overall pelvic floor muscle function and strength
Reduced risk of future pelvic floor issues
Treatment of Specific Dysfunctions
Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction is a common condition where a man is unable to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse. Pelvic floor physical therapy (PFPT) can be an effective treatment for this dysfunction. PFPT techniques such as pelvic floor muscle exercises, biofeedback, and manual therapy can help improve blood flow and muscle function in the pelvic region, leading to improved erectile function.
Expected outcomes of PFPT for erectile dysfunction may include increased ability to achieve and maintain an erection, improved sexual satisfaction, and increased confidence and self-esteem. A case study from our clinic of a 45-year-old man with erectile dysfunction showed significant improvement in erectile function after 12 weeks of PFPT, with the patient reporting increased frequency and quality of erections.
Premature Ejaculation
Premature ejaculation is a common sexual dysfunction where a man ejaculates too quickly during sexual activity, often before he or his partner is satisfied. PFPT can be an effective treatment for this condition by addressing underlying pelvic floor muscle dysfunction and improving control over ejaculation.
PFPT techniques used for premature ejaculation may include pelvic floor muscle exercises, relaxation techniques, and behavioral therapy. Expected outcomes of PFPT for premature ejaculation may include improved control over ejaculation, increased sexual satisfaction, and improved relationship dynamics.
Peyronie's Disease
Peyronie's disease is a condition where scar tissue forms in the penis, causing it to curve or bend during erections. This can lead to pain, difficulty with intercourse, and psychological distress. PFPT can be an effective treatment for Peyronie's disease by addressing pelvic floor muscle dysfunction and improving penile blood flow.
PFPT techniques used for Peyronie's disease may include pelvic floor muscle exercises, manual therapy, and stretching techniques. Expected outcomes of PFPT for this condition may include reduced pain, improved penile curvature, and improved sexual function.
Other Dysfunctions
In addition to the above-mentioned dysfunctions, PFPT can also be beneficial for other pelvic floor-related dysfunctions such as urinary incontinence, pelvic pain, and post-prostatectomy dysfunction. PFPT techniques used for these conditions may include pelvic floor muscle exercises, biofeedback, and manual therapy.
Expected outcomes of PFPT for these dysfunctions may include improved bladder control, reduced pain, and improved sexual function.
Conclusion
Recap of main points
Throughout this article, we have discussed the anatomy of the penis and various dysfunctions that can occur. We have learned about the importance of the corpora cavernosa, corpus spongiosum, and the urethra in maintaining a healthy and functional penis. We have also explored common dysfunctions such as erectile dysfunction, Peyronie's disease, and premature ejaculation.
It is important to remember that these dysfunctions can have a significant impact on a person's physical and emotional well-being. They can also affect relationships and overall quality of life. Therefore, it is crucial to seek treatment if you are experiencing any of these issues.
Importance of seeking treatment for penis dysfunctions
Many people may feel embarrassed or ashamed to seek treatment for penis dysfunctions. However, it is essential to understand that these dysfunctions are common and can be effectively treated with the help of a pelvic floor physical therapist (PFPT).
Ignoring these dysfunctions can lead to worsening symptoms and potentially more severe complications. Seeking treatment from a PFPT can not only improve physical symptoms but also provide support and education on how to manage and prevent future dysfunctions.
Benefits of PFPT for treating penis dysfunctions
PFPTs are trained professionals who specialize in treating pelvic floor dysfunctions, including those related to the penis. They use a variety of techniques, such as manual therapy, exercises, and biofeedback, to address the root cause of the dysfunction and improve overall function and quality of life. Additionally, PFPTs can also provide education on lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise, that can help manage and prevent future dysfunctions.
If you are experiencing pelvic floor dysfunctions associated with the issues above, please reach out to us at Pelvic Health Center in Madison, NJ to set up an evaluation and treatment! Feel free to call us at 908-443-9880 or email us at receptionmadison@pelvichealthnj.com.
Read More:
How Chronic Pelvic Congestion in Men Contributes to Prostatitis By Shannon Strauch, PTA, STMT-1 on 12/11/2024 How lymphatic issues can cause symptoms of prostatitis Prostatitis and Tight Pelvic Floor Muscles: A Comprehensive Guide By Shannon Strauch, PTA, STMT-1 on 12/10/2024 How a tight pelvic floor can be the reason for prostatitis symptoms
Are you ready to live pain free?
Request An Appointment