Back
What Pelvic Floor Muscles are in Control of Erection and Ejaculation?
By Shannon Strauch, PTA, STMT-1 on 8/23/2024

Male sexual function is a complex interplay of anatomical structures and physiological processes. Among the many muscles involved, the ischiocavernosus and bulbospongiosus muscles are crucial yet often overlooked components. These muscles not only contribute to the mechanics of erection and ejaculation but also play a vital role in overall sexual health. Understanding their function and how pelvic floor therapy can address dysfunctions related to these muscles is key to maintaining optimal sexual well-being.
Anatomy and Function
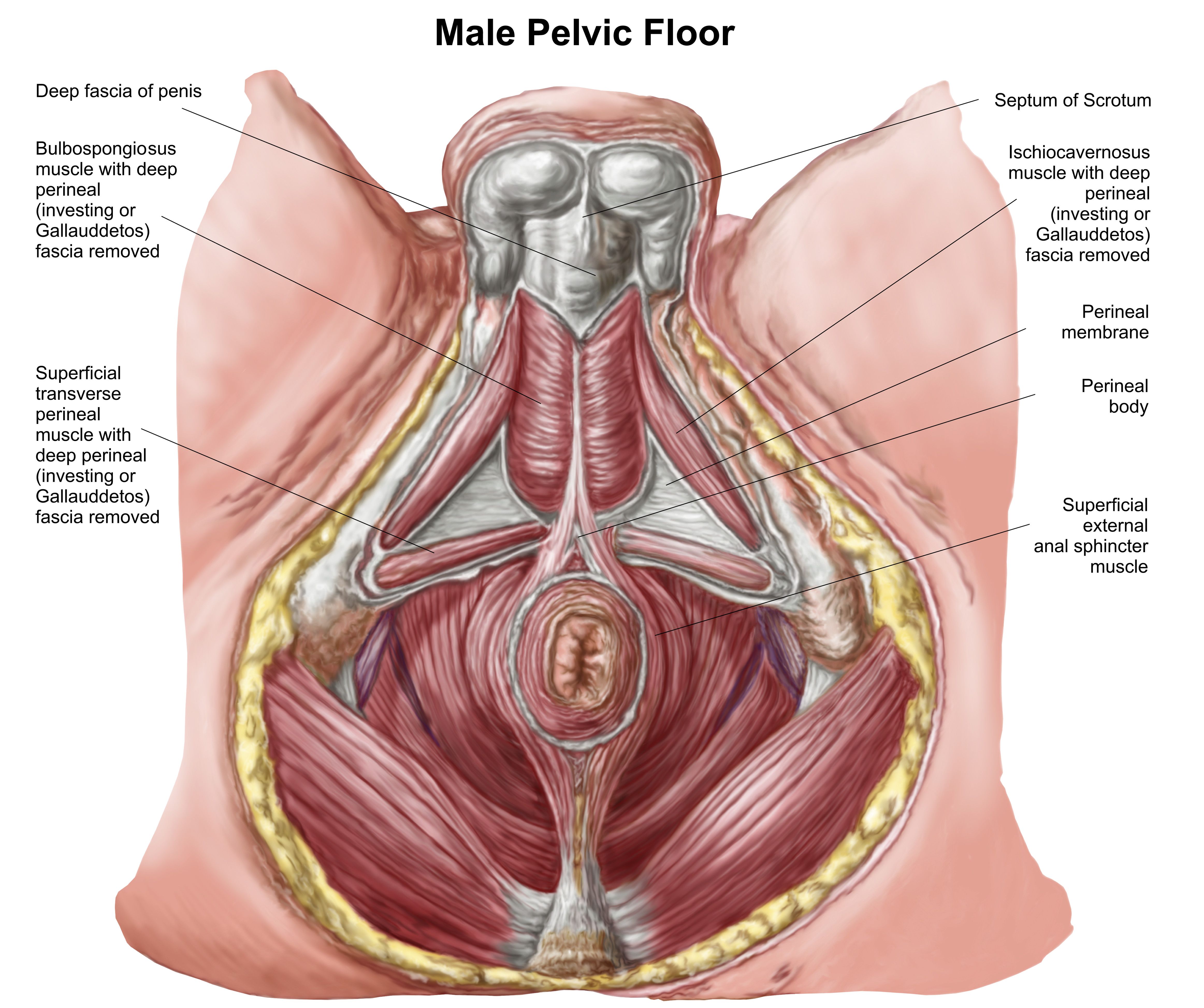
Ischiocavernosus Muscle:
The ischiocavernosus muscle is located in the perineum, attached to the ischial tuberosities (the sit bones) and extending to the base of the penis, where it envelops the crus (the root of the penis). Its primary function is to compress the crus during an erection, trapping blood within the corpora cavernosa, the sponge-like regions of the penis that fill with blood to create an erection. By compressing these areas like a tourniquet, the ischiocavernosus muscle helps maintain penile rigidity, ensuring that the erection is sustained during sexual activity.Bulbospongiosus Muscle:
Situated in the midline of the perineum, the bulbospongiosus muscle surrounds the bulb of the penis and the corpus spongiosum, the tissue that houses the urethra. This muscle is instrumental in ejaculation, as it contracts rhythmically to propel semen through the urethra. Additionally, it aids in emptying the urethra after urination by compressing the bulb of the penis. The strength and coordination of the bulbospongiosus muscle are essential for effective ejaculation and urinary function.Role in Erection
The ischiocavernosus and bulbospongiosus muscles work in tandem to facilitate and sustain an erection. During sexual arousal, these muscles contract, trapping blood in the penis's erectile tissues. The ischiocavernosus muscle compresses the veins in the crus, preventing blood from leaving the corpora cavernosa, which helps maintain the erection. The bulbospongiosus muscle also contributes by increasing the pressure within the corpus spongiosum, ensuring the erection remains firm.
Role in Ejaculation
Ejaculation is a finely tuned process that relies on the coordinated action of several pelvic floor muscles, with the bulbospongiosus playing a leading role. As sexual climax approaches, the bulbospongiosus muscle contracts rhythmically, creating waves of pressure that force semen through the urethra and out of the penis. This muscle's contraction is not only crucial for the physical expulsion of semen but also enhances the sensation of orgasm, contributing to sexual satisfaction.
Common Dysfunctions
Dysfunctions in the ischiocavernosus and bulbospongiosus muscles can lead to significant sexual health issues:
Ischiocavernosus Dysfunction:
When the ischiocavernosus muscle is weak or overly tight, it can compromise the ability to maintain an erection. Weakness in this muscle may result in insufficient compression of the crus, leading to a loss of penile rigidity during sexual activity. On the other hand, hypertonicity (excessive tightness) can cause discomfort or pain during erections, further impacting sexual performance.Bulbospongiosus Dysfunction:
Weakness in the bulbospongiosus muscle can affect the force and control of ejaculation. This may result in a reduced ejaculatory force or difficulty in achieving complete ejaculation, potentially leading to fertility concerns or decreased sexual satisfaction. Additionally, dysfunction in this muscle can interfere with the proper emptying of the urethra after urination, increasing the risk of post-void dribbling.How Pelvic Floor Therapy Can Help
Pelvic floor therapy offers a targeted approach to addressing dysfunctions in the ischiocavernosus and bulbospongiosus muscles, helping to restore normal function and improve sexual health.
Evaluation and Assessment:
A comprehensive evaluation by a pelvic floor therapist can identify specific dysfunctions in these muscles. This assessment may include a physical examination, muscle strength testing, and, if necessary, imaging studies to determine the extent of the dysfunction.Treatment Approaches:
Pelvic floor therapy involves a combination of exercises, manual therapy, and biofeedback techniques to target these muscles. Strengthening exercises can improve the power and endurance of the ischiocavernosus and bulbospongiosus muscles, while relaxation techniques can alleviate hypertonicity. Biofeedback can help patients gain better control and coordination of these muscles, enhancing their function during sexual activity.Integration with Comprehensive Care:
Pelvic floor therapy is often part of a multidisciplinary approach to treating sexual dysfunction. Collaboration with urologists, endocrinologists, or other specialists may be necessary to address underlying conditions contributing to muscle dysfunction, such as hormonal imbalances, nerve damage, or vascular issues.Conclusion
The ischiocavernosus and bulbospongiosus muscles are integral to male sexual function, playing key roles in erection and ejaculation. Dysfunction in these muscles can lead to significant sexual health challenges, but pelvic floor therapy offers effective solutions. By strengthening, relaxing, and improving the coordination of these muscles, individuals can regain control over their sexual health and enhance their quality of life. If you are experiencing sexual dysfunction, reach out to us at Pelvic Health Center in Madison, NJ to set up an evaluation and treatment! Feel free to call us at 908-443-9880 or email us at receptionmadison@pelvichealthnj.com.
Read More:
How Chronic Pelvic Congestion in Men Contributes to Prostatitis By Shannon Strauch, PTA, STMT-1 on 12/11/2024 How lymphatic issues can cause symptoms of prostatitis Prostatitis and Tight Pelvic Floor Muscles: A Comprehensive Guide By Shannon Strauch, PTA, STMT-1 on 12/10/2024 How a tight pelvic floor can be the reason for prostatitis symptoms
Are you ready to live pain free?
Request An Appointment